Your information security and privacy protection in order
Information security
The internet is more present than ever. Almost every organisation uses an e-mail client, website and other online tools such as a CRM system. This means that a large amount of information is stored and exchanged digitally and online. This needs to be done securely and can only be done on the basis of strict information security.
Properly designing information security involves applying a wide range of measures to reduce risks.
It is insufficient for organisations to just know that they need to do information security, they need to have tools at their disposal that will help them in the execution of business processes, internal operations and strategic decision-making.
Page overview
What is information security?
In simple terms, information security is the mapping and assessment of all processes surrounding information within an organisation. This is often done through an Information Security Management System (ISMS). Among other things, this identifies processes and regularly monitors them for potential risks or threats.
For many organisations, information security is a burden rather than a blessing. Employees feel restricted in the flexibility of performing their jobs. In addition, the media also devotes so much attention to privacy protection and information security that in some situations even aversion to the subject arises.
Why is information security important?
Yet information security is desperately needed. In recent years, more than four in 10 companies have experienced cybercrime. The actual number of organisations affected is probably much higher, for example because almost 10 per cent of organisations have no idea whether a data breach has occurred within the organisation at all.
Keeping your information security under control is no easy task. After all, to ensure security, you need to go through the process structurally.
Get full control of your information security
Information security basics
Information security is a broad term. It covers many things within your organisation. If you want to get started with information security, the scope may put you off.
To start with the basics of information protection, we will take a closer look at the core process. Too often, information security is thought to be a one-off task. However, this is not the case. The core process needs to be gone through repeatedly and consists of the following steps:
- Inventory information and its value to all stakeholders (= identify ‘crown jewels’)
- Analyse risks to this information
- Implementing measures to reduce the risks
- Check effectiveness of measures
What are the 3 basic principles of information security?
Over time, more and more reliability requirements around information security have emerged. These include three basic principles of information security and legislations (such as the GDPR).
To determine the intended level of your information security, the reliability requirements to be met will be determined. Generally, this classification is done according to the CIA-triad, looking at the following three aspects:
- Availability. Authorised users have access to information and/or systems at the right times.
- Integrity. Ensuring the accuracy, timeliness (topicality) and completeness of information and its processing.
- Confidentiality. Ensuring accessibility of information only to those authorised to do so.
Information security and privacy
Information security and privacy go hand in hand. In fact, one cannot exist without the other. With the advent of the GDPR, awareness has increased and there are more requirements for information security.
As indicated above, privacy and information security are closely linked. After all, privacy protection is about the confidentiality of personal data and how to protect it - i.e. information security. On the other hand, almost all information contains more or less sensitive personal data, so protecting the privacy of data subjects is an aspect to consider.
What is the difference between information security and privacy?
Nevertheless, differences between privacy and information security can also be distinguished:
- Information security is primarily about availability, integrity and confidentiality of information in processes and systems.
- Privacy protection is about data subjects' rights, lawfulness of processing, transparency and protection of personal data.
Risk management
It is more important than ever to identify risks and threats. With all the digital possibilities, it is important to secure information properly.
There are numerous threats that can cause your organisation to run into trouble. Threats that are important for your information security risk management include:
- Incidents and incident handling
- Misuse
- Unauthorised access
- Information sharing and retention
- Mobile devices and teleworking
- System and user errors
- Physical security
- Responsibility
- Laws and regulations
- Business continuity
With all the digital possibilities, it is important to secure information properly. With mapping, you prepare yourself well for possible consequences and can possibly reduce the risk posed by the threats.
Over 40 pages on information security.
Information security risk analysis
From the moment business is started, opportunities for threats and risks related to information security arise. To protect sensitive information, adequate risk management within an organisation is important. But what is a good way to identify and manage risks within information security?
The most practical way to identify and control risks within information security is by using an Information Security Management System (ISMS) based on ISO 27001, for example. An ISMS covers all the issues and practices for securing all (confidential) information within your organisation. This is often supported with the use of an ISMS tool, such as Base27.
When an organisation works with information, there will always be risks lurking. This is the case in every organisation, think for example of personal data, process information or manuals of a particular product or service. As an organisation, you want to mitigate the risks. But how do you know what risks there are? For this, you can carry out an information security risk analysis.
Conducting risk analysis
It is important to carry out a risk analysis with a group of involved/experienced people (rather than by one or two people). This gives a sharper picture of the risks, allows for discussion and the final result is often more complete and reliable. It also provides a good starting point for taking action on the risks; there is greater understanding and support.
The main points in a row:
- Agree on probability and impact for the organisation regarding risks;
- Establish the scope for a risk analysis;
- Designate a responsible party (based on the scope);
- Involve concerned/experienced persons in the analysis;
- Choose an appropriate threat model if required;
- Identify risks for relevant threats and determine probability and impact;
- Take measures for the unacceptable risks.
Threats in perspective
In as many as 70% of all information security incidents, the actions of in-house staff are found to be part of the cause. Examples include losing a laptop or phone, clicking on a link from a spam e-mail or sending sensitive information to the wrong person.
Of course, there is also significant risk at the technical level, where today's measures may be insufficient for tomorrow's threats.
Especially for smaller organisations, it is difficult to have an appropriate response in this dynamic. The challenge scares and makes one uncertain about what is needed and how to achieve it. The knowledge for this is often insufficient and time and costs are also a considerable barrier.
The choice is then obvious to do little or nothing and to accept the risk of damage as a result of such incidents. After all, doing business is taking risks.
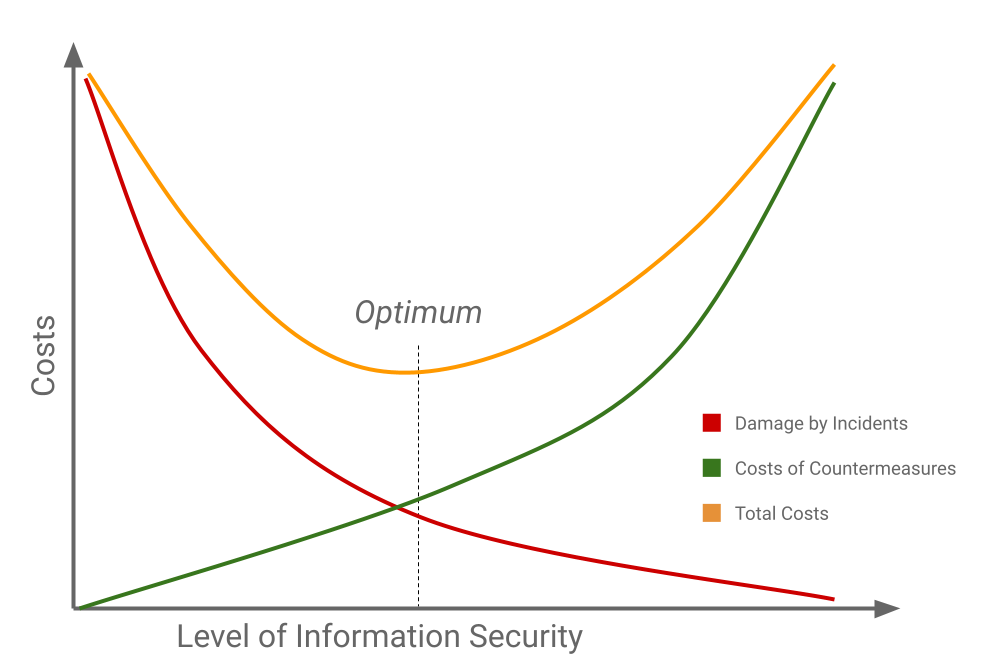
Yet the costs and time required for an adequate level of security need not be great and may even be a saving. If you plot the potential damage against the cost of prevention, there is a clear optimum.
Optimum
As a business owner, you are used to weighing the level of measures and the costs you incur against the benefits: savings from any incidents. That potential damage is different for every organisation and so is the level of measures to be taken. As an indication, SMEs lose almost €79,000 on average per digital intrusion.
Information security awareness
Awareness of the risks surrounding information security is essential for organisations. Yet information security is much more extensive than is often thought. Not surprisingly, essential components are sometimes overlooked.
Your organisation's information security is only as strong as its weakest link. You can have everything in order, but any weakness can bring down the entire reliability of information security. Awareness of information security is therefore important. In practice, human actions are the weakest link in most situations.
So this means that the actions of your employees are the biggest risk in protecting and securing sensitive information or personal data. It is therefore essential to make all employees in your organisation aware of the risks surrounding information security, make mutual agreements on desired behaviour and respect confidentiality - where necessary.
Information security policy
Information security policies are really not a luxury for organisations. The objectives and measures you need to achieve for your information security are included in this article and are based on ISO 27001. Therefore, these objectives and measures are relevant to every industry.
What is the information security policy?
The main reason to have an information security policy in place is to minimise the risk and damage caused by incidents and thus ensure the continuity of your business. But how do you put together a good information security policy? This is best done on the basis of four main lines:
- Determine context;
- Identify stakeholders and their interests;
- Define objectives;
- Define roles and responsibilities.
What is the CIA model of information security?
When it comes to information security, the so-called CIA-triad is used. Here, CIA stands for Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability.
When talking about information classification, this refers to indicating the importance to users of the information based on the various aspects such as availability, integrity and confidentiality (CIA). Each aspect of classification needs its own requirements and measures when it comes to using and/or preserving (storing) the information.
Roles and responsibilities information security
From protecting sensitive data to implementing robust security measures; a crucial task rests on the shoulders of those charged with ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of information.
Who is responsible for information security?
When everyone in an organisation is aware of their specific roles and responsibilities in relation to information security, the chances of misunderstandings and negligence are significantly reduced.
A clear investment of responsibilities not only creates transparency within an organisation, but also promotes team commitment to protecting sensitive information.
Information security plan/operational planning
Information security is about availability, integrity and confidentiality of (privacy) sensitive information. Because it is a comprehensive process, it can be difficult to decide where to start setting up or maintaining information security. An information security plan can help you with this.
Organisations often do something about information security. Yet in most cases, a structural approach is lacking. Certain security activities are carried out on a one-off basis, but without interconnection and regular follow-up. They do not appear structurally on the agenda and the activities that are taken up are not described anywhere.
An information security plan - or operational planning - can help your organisation draw up the objectives related to information security in coherence and implement security activities structurally.
Annual information security activities
Information security is a process that requires regular time and attention. Are there any new developments or risks you need to consider? Are the measures taken still adequate? Are the measures working effectively and are you still ‘in control’? Such questions require looking at how things are going and what, if anything, needs to be adjusted.
This involves all kinds of activities that need to be carried out on a regular basis. If you want to create such an annual planning around information security for your organisation, it is important to do this in the right way. Each component should be sufficiently addressed so that risks remain manageable and the risk of incidents is reduced.
Information security standard
Poor information security can have major consequences for organisations. Not only financially, but also when it comes to customer data, customer trust in the organisation and sometimes an organisation can even temporarily shut down. As awareness of the possible consequences increases, information security is starting to play an increasingly important role within organisations.
To be sure of information security, standards and certifications have been created, for example ISO 27001 and NEN 7510.
Information security and ISO 27001
As an organisation, there are various ways of doing information security. Some organisations are expected to comply with a certain standard. ISO 27001 is available for this purpose. This standard provides guidelines around information security within the organisation. If this is met, the organisation can receive certification.
Information security and NEN 7510
Specific rules apply to organisations within healthcare. These organisations are obliged to maintain strict information security. They demonstrate this with a NEN 7510 certification.
Information security advice
Good information security is essential for any organisation. Not only do your customers expect good information security from the organisation they share sensitive data with. The government also imposes increasingly strict requirements on this.
Implementation of security standards such as ISO 27001, NEN 7510 or the AVG require specialist knowledge in the field of IT, business and legal matters. Because these security standards affect almost all aspects of business operations, it is difficult to organise this and keep an overview.
Good ISMS software can help you with this.
To demonstrably comply with the extensive standards frameworks, it is also essential to have a clear structure and to administer matters centrally. Think, for instance, of an authorisation matrix. An ISMS provides support for this in a clear manner.
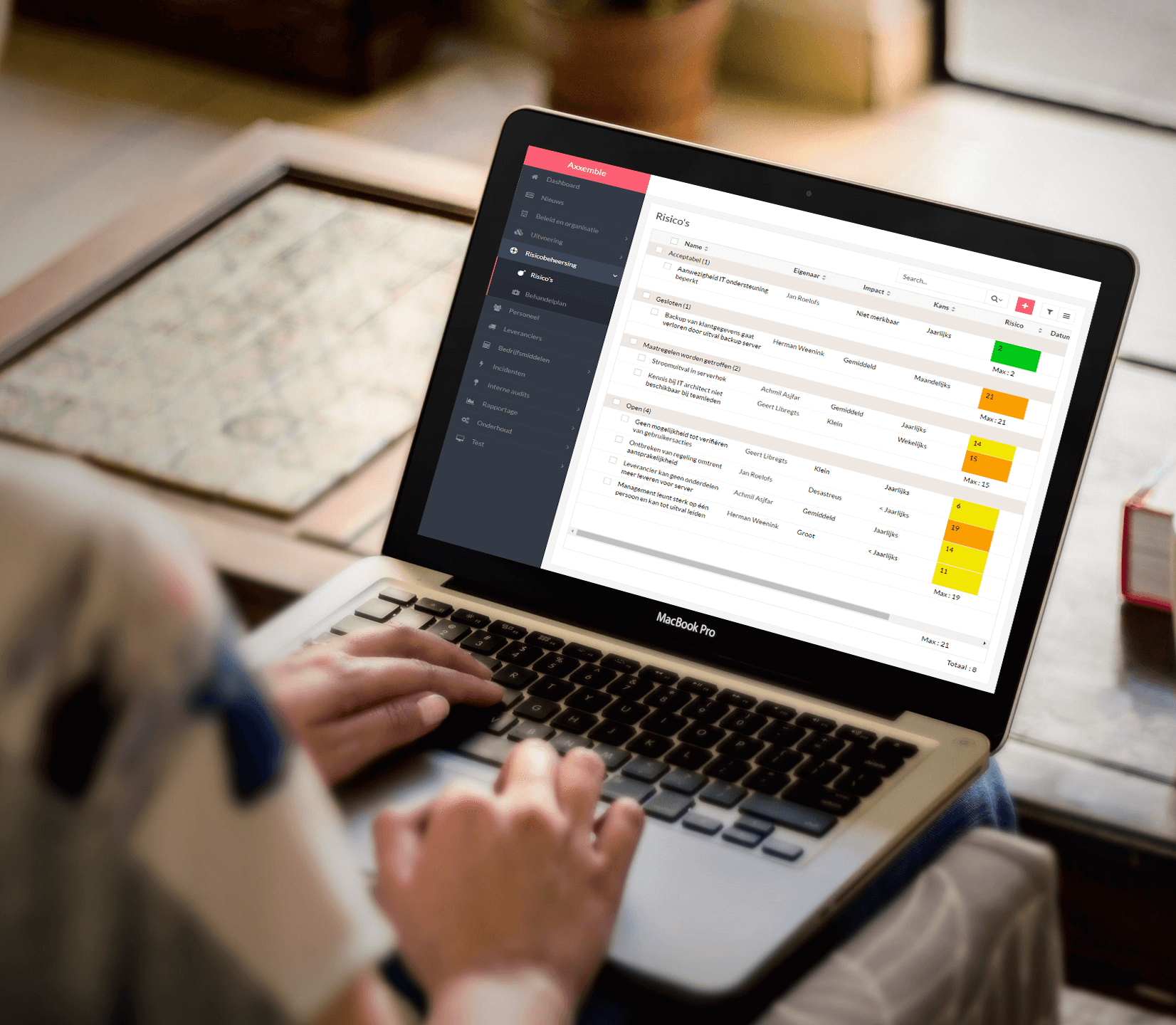
Base27
Axxemble aims to support organisations in small and medium-sized enterprises in a smart and practical way to ensure adequate information security. We do this by making the aforementioned questions central to our solution, Base27.
Our online software tooling provides a framework (ISMS) for policy and organisation around information security, risk management, description of processes and procedures and support for conducting the various registrations.
Using Base27, you are able to quickly set up information security around the desired standard, including support for the new privacy legislation.

 English
English
 Nederlands
Nederlands